

There are many methods used to solve this task. The task of the neural network is to find the inverse function of degradation using just the HR and LR image data. The degradation parameters D and $\sigma$ are unknown only the high resolution image and the corresponding low resolution image are provided. Low resolution images can be modeled from high resolution images using the below formula, where D is the degradation function, I y is the high resolution image, I x is the low resolution image, and $\sigma$ is the noise.
#ML SUPER RESOLUTION FOR FREE#
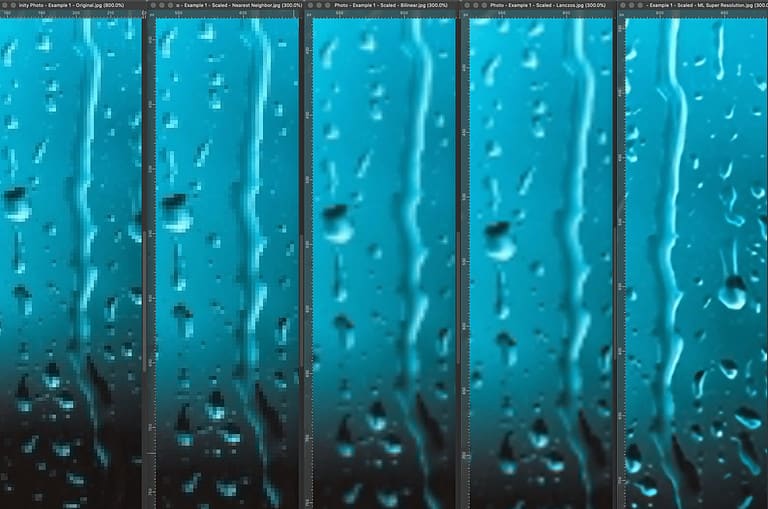
You can also run the code for one of the models we'll cover, ESPCN, for free on the ML Showcase. In this article we will discuss the theory involved, various techniques used, loss functions, metrics, and relevant datasets.
Image Super Resolution refers to the task of enhancing the resolution of an image from low-resolution (LR) to high (HR).
#ML SUPER RESOLUTION SOFTWARE#
The dataset is available at this https URL and the software package at this https URL. High-resolution Airbus imagery is CC BY-NC, while the labels and Sentinel2 imagery are CC BY, and the source code and pre-trained models under BSD. We illustrate this specific point by training and releasing several highly compute-efficient baselines on the task of Multi-Frame Super-Resolution. We hereby hope to foster broad-spectrum applications of ML to satellite imagery, and possibly develop from free public low-resolution Sentinel2 imagery the same power of analysis allowed by costly private high-resolution imagery. We accompany this dataset with an open-source Python package to: rebuild or extend the WorldStrat dataset, train and infer baseline algorithms, and learn with abundant tutorials, all compatible with the popular EO-learn toolbox.
We temporally-match each high-resolution image with multiple low-resolution images from the freely accessible lower-resolution Sentinel-2 satellites at 10 m/pixel. We also enrich those with locations typically under-represented in ML datasets: sites of humanitarian interest, illegal mining sites, and settlements of persons at risk. The largest and most varied such publicly available dataset, at Airbus SPOT 6/7 satellites' high resolution of up to 1.5 m/pixel, empowered by European Space Agency's Phi-Lab as part of the ESA-funded QueryPlanet project, we curate nearly 10,000 sqkm of unique locations to ensure stratified representation of all types of land-use across the world: from agriculture to ice caps, from forests to multiple urbanization densities. To remediate this, we introduce here the WorldStrat dataset.
#ML SUPER RESOLUTION PDF#
Download a PDF of the paper titled Open High-Resolution Satellite Imagery: The WorldStrat Dataset - With Application to Super-Resolution, by Julien Cornebise and Ivan Or\voli\'c and Freddie Kalaitzis Download PDF Abstract:Analyzing the planet at scale with satellite imagery and machine learning is a dream that has been constantly hindered by the cost of difficult-to-access highly-representative high-resolution imagery.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
